The Significance of Nitric Oxide
1 person dies from vascular disease every 6 seconds worldwide*
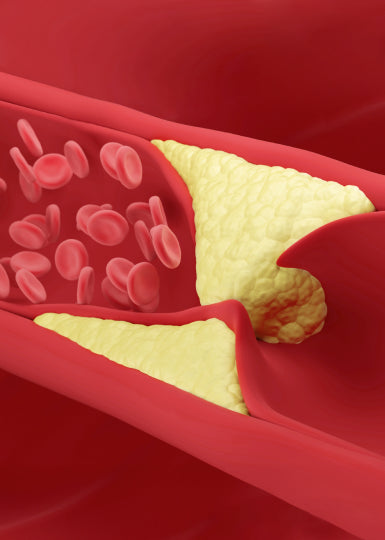
The cause of “vascular disease,” which has the highest mortality rate worldwide and the highest disease burden in Korea, is the decrease in nitric oxide production in the body due to aging.
(* Source: 2019 World Health Organization (WHO) vascular disease mortality statistics)
Why Nitric Oxide Production Declines
Nitric oxide, which keeps blood vessels healthy, is produced by the vascular endothelial cells in the arteries. However, as we age and the vascular endothelial cells become damaged, they cannot produce enough of the necessary nitric oxide, making us vulnerable to vascular disease.
* Cross-section of blood vessels by age
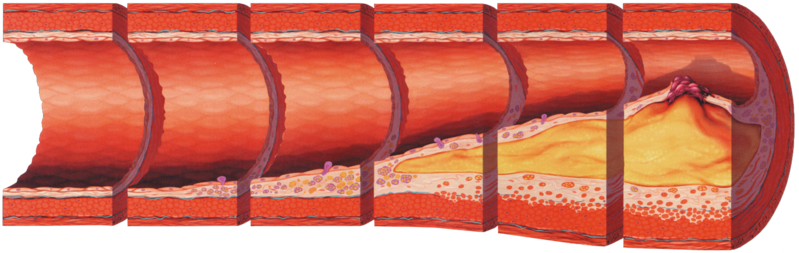
10-20s
Vascular damage 0%
30-40s
Vascular damage 20%
50-60s
Vascular damage 50%
70s
Vascular damage 85%
As we age, the vascular endothelial cells that produce nitric oxide become damaged, and nitric oxide levels drop below 15%, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Nitric oxide is produced by the endothelial cells of the arteries and performs signaling and other functions necessary for our body.
History of Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide research has led to important developments in various fields such as biology, medicine, and pharmacy since the 1980s. Nitric oxide is an important research subject in the field of life sciences, and it is expected to contribute to the treatment and prevention of various diseases in the future.
Signaling Molecule of Life, Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide is an essential signal molecule that plays an important role in various biological systems, opening up new possibilities for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. In particular, it has been revealed that nitric oxide plays an important role in various biological systems such as vascular health, the immune system, the nervous system, and the digestive system.
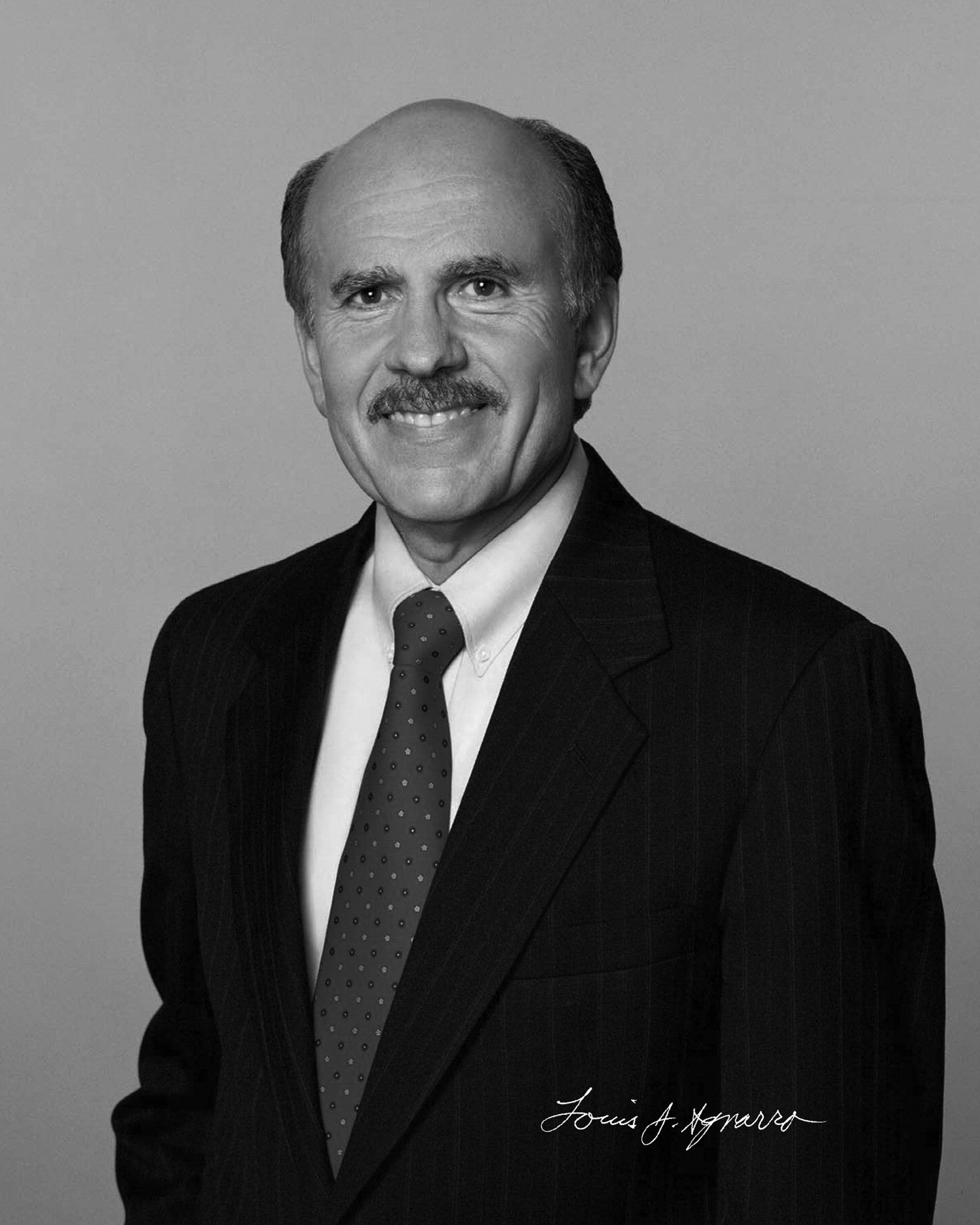

"Nitric oxide discoveries have opened new avenues for patient treatment."
Dr. Louis J. Ignarro (UCLA School of Medicine)
1998 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the discovery of 'Nitric Oxide'
The Significance of Nitric Oxide
The cause of 'vascular disease', which has the highest mortality rate worldwide and the highest disease burden in Korea, is that nitric oxide, a substance that helps blood vessels relax, decreases as aging progresses.